In their quest to try and find some sort of evolutionary similarity between humans and apes, scientists have compared DNA, proteins, anatomy, behavior, and every other conceivable feature. But many of these attempts showed that a huge chasm of dissimilarity exists with no distinct evolutionary connection. And now, a new study comparing saliva between humans and apes is once again showing the uniqueness of humans and the failure of evolutionary reasoning.1
Your saliva is a highly designed and precise combination of important proteins required for preprocessing food in your mouth prior to entering your digestive tract. Human saliva also contains other specific types of proteins needed for the maintenance of tooth mineralization and protection from microbial pathogens. The sum total of the complement of proteins in saliva is called the salivary proteome.
In a recent research study, scientists compared the salivary proteomes of humans with two ape species considered to be our closest living evolutionary relatives: chimpanzees and gorillas. They also included monkeys (Rhesus macaque) as an evolutionary out-group—an alleged distant relative.
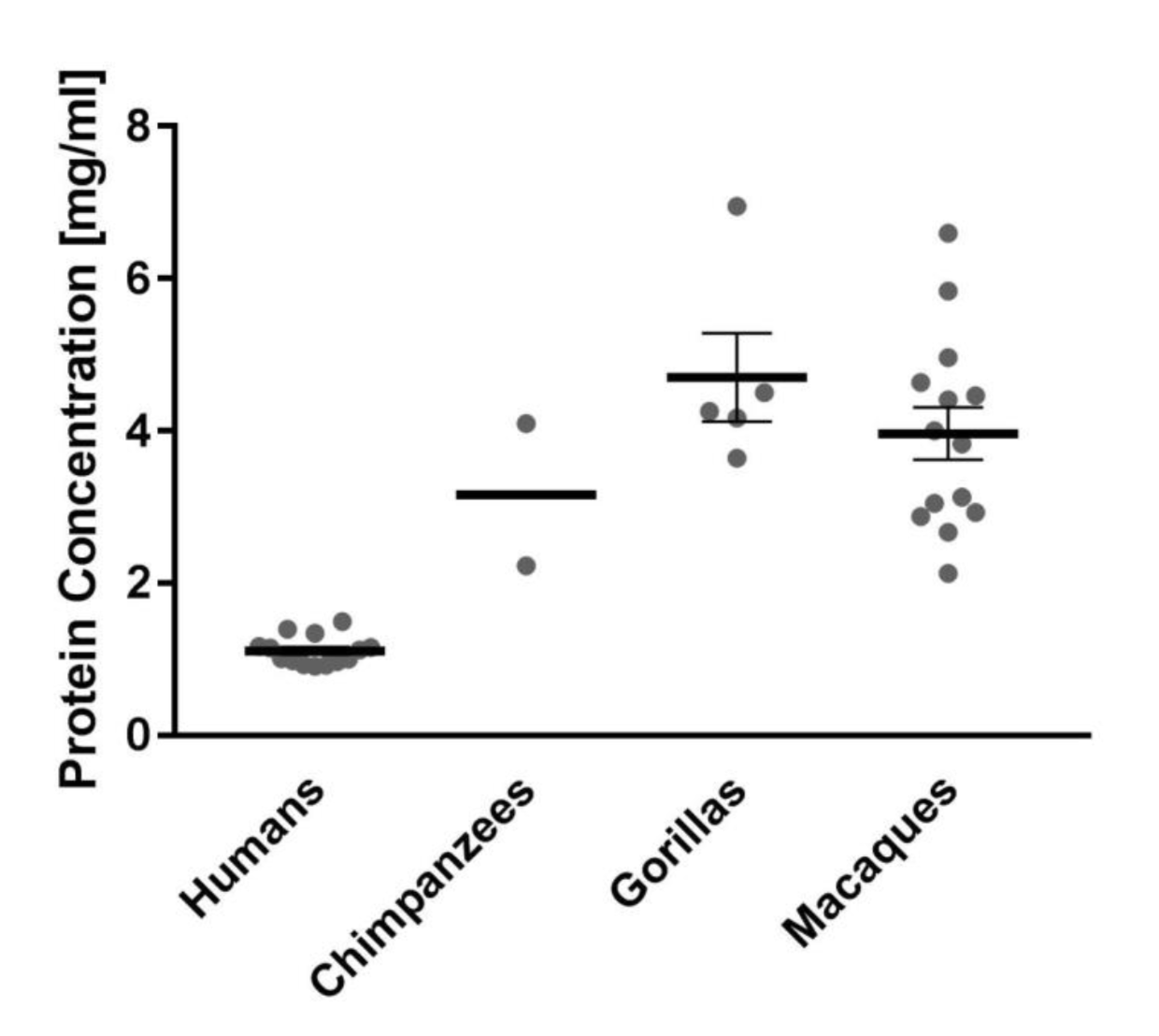
The first major difference the researchers noted was that human saliva is much more watery and diluted than apes’ and the overall concentration of proteins is much lower. In fact, human saliva contains half the total amount of proteins compared to apes and macaques (see figure).
The next thing the scientists observed was that the concentrations of the major groups of proteins is markedly different between humans and apes as well. The researchers also noted that human-specific proteins were found that do not exist in apes. Overall, the salivary proteomes were distinctly different between not just humans and apes, but also between chimps, gorillas, and macaques.
In their conclusion, the researchers stated, “We discovered unique protein profiles in saliva of humans that were distinct from those of nonhuman primates.” They also claimed, “Certain properties and components of human and nonhuman primate saliva might have evolved in a lineage-specific manner.”1 The term “lineage specific” means there is no evolutionary overlap; each human, ape, and monkey salivary proteome is unique.
This observance doesn’t line up with evolution, but fits well with Genesis that tells us God created each type of creature after its kind.2 Humans, chimps, gorillas, and macaques are unique kinds, and both science and scripture continue to confirm this biological truth.
References
1. Thamadilok, S. et al. 2020. Human and Nonhuman Primate Lineage-Specific Footprints in the Salivary Proteome. Molecular Biology and Evolution. 37 (2): 395-405.
2. Genesis 1:21, 25
Dr. Tomkins is Life Sciences Director at the Institute for Creation Research and earned his doctorate in genetics from Clemson University.

Ape Spit Radically Different from Human
The Latest
Where Paleontology Fails, Paleo-Robots Avail
A Phys.org science article begins with what could be read as a religious story that occurred a long, long time ago.
Life on Earth started in the...
Puzzling Fossils at an Unlikely Time
Wherever and whenever life is found, it is incredibly complex. This certainly applies to cyanobacterial photosynthetic life that supposedly were some...
CREATION PODCAST
A Theory Designed to Be...Anti-Design | The Creation Podcast:...
Science is objective. At least, that’s what we’re told. But there are inherent issues with this statement that can...
Seeing the Case for Creation in Fruit Flies
Our brain is designed to smoothly and constantly process what we see via the incredibly sensitive photoreceptors (cones and rods) of our eyes.1...
Amazing Defense Systems
Bacteria (prokaryotes) are ubiquitous. A fraction cause disease in people, animals, and plants, but the majority are the foundation for the global food...
Octopus and Fish Plan a Complex Coordinated Hunt
The octopus—an invertebrate—never fails to surprise researchers with its incredible abilities.1,2
The octopus was designed...
A ''40 million year old'' 100% European Gnat
Finding well-preserved creatures in amber1 is a landfall for creation scientists, much like the numerous discoveries of soft dinosaur tissue...
CREATION PODCAST
The Undeniable Power of Narrative | The Creation Podcast: Episode...
Science is objective. At least, that’s what we’re told. But there are inherent issues with this statement that can cause...
Paintbrush of the Creator
Who doesn’t enjoy the amazing color patterns of butterflies?1,2 Such beautiful designs and construction do not reflect blind naturalistic...